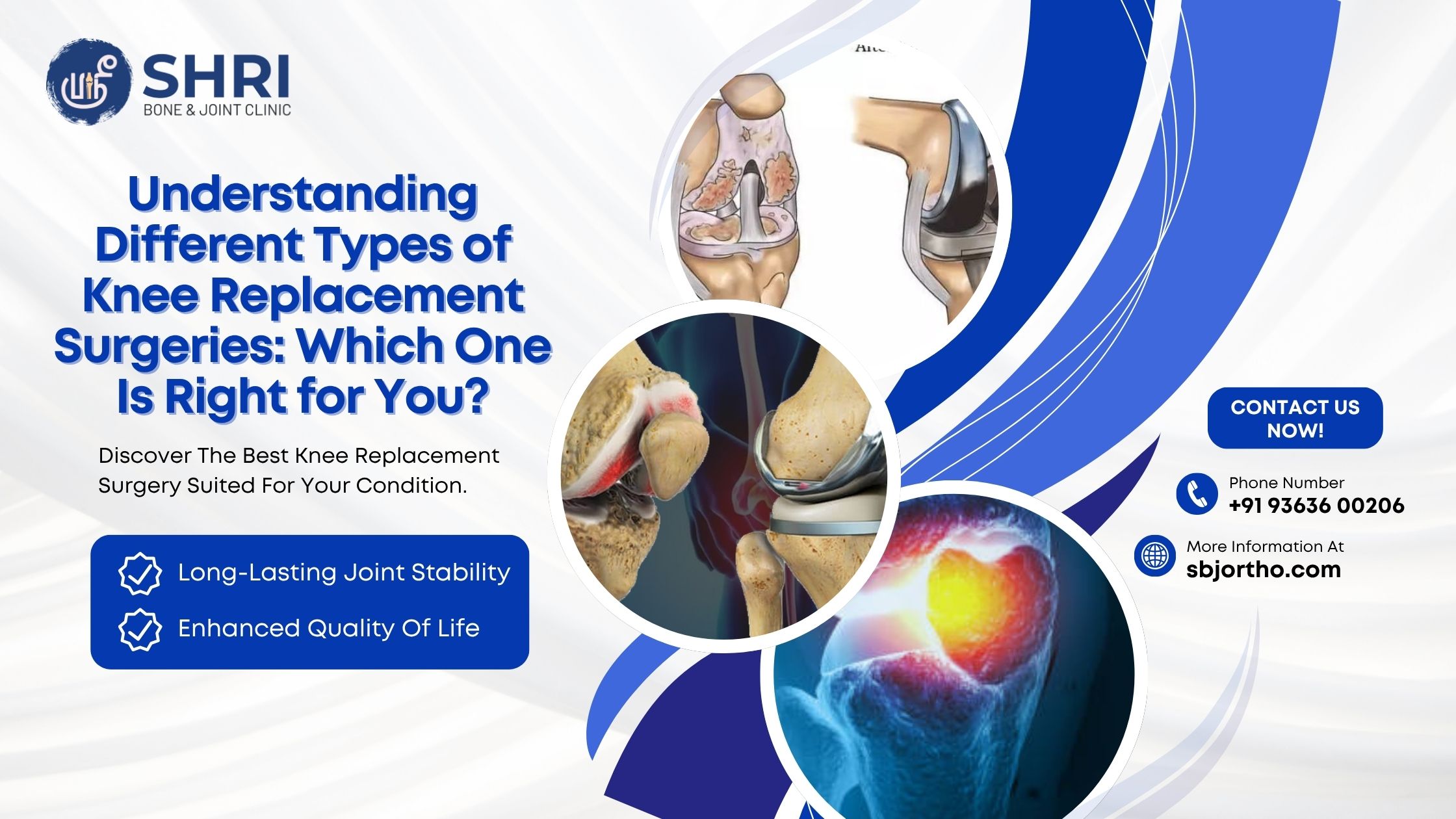
Knee replacement surgery has transformed the lives of millions by restoring mobility and eliminating chronic joint pain. Yet, for many patients, the variety of surgical options available today can feel overwhelming. From partial procedures to fully robotic ones, each technique offers unique advantages based on your age, condition, and lifestyle.
This article breaks down the different types of knee replacement surgeries so you can better understand what each one involves—and which might be right for you.
Why Do Patients Need Knee Replacement Surgery?
Knee replacement is usually recommended when the cartilage cushioning the knee joint wears down due to osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, or injury. As cartilage degenerates, bones rub against each other, causing stiffness, swelling, and constant pain.
When medications, physiotherapy, and injections no longer provide relief, replacing the damaged surfaces with artificial implants becomes the most effective solution. The goal is to restore alignment, improve stability, and help patients return to a pain-free, active life.
1. Total Knee Replacement – The Complete Joint Solution
Total Knee Replacement is the most common form of knee surgery. In this procedure, the surgeon replaces the entire knee joint—both femoral (thigh bone) and tibial (shin bone) surfaces—along with the underside of the kneecap if needed.
Modern implants are made from durable metals and medical-grade plastics that mimic natural motion. Total replacement is typically recommended for people with severe arthritis affecting multiple parts of the joint or those whose mobility is significantly restricted.
Key benefits:
- Complete relief from pain and stiffness
- Long-term durability (often 20+ years)
- Predictable recovery with physiotherapy
- Suitable for both older and younger patients with advanced damage
Best for: Patients whose arthritis involves the entire knee or who have failed all non-surgical treatments.
2. Partial Knee Replacement – Targeted Treatment for Localized Damage
When only one section of the knee joint is damaged, a Partial Knee Replacement (also called unicompartmental arthroplasty) can be an ideal solution.
Instead of replacing the entire joint, only the affected compartment—either the inner (medial) or outer (lateral) portion—is resurfaced with an implant.
Because most of the bone, cartilage, and ligaments remain untouched, this surgery preserves natural movement and typically results in quicker recovery and less pain.
Key benefits:
- Smaller incision and minimal blood loss
- More natural knee function
- Shorter hospital stay and faster recovery
- Easier future revision if needed
Best for: Patients with arthritis limited to one compartment of the knee.
3. Robotic Knee Replacement Surgery – Precision and Personalization
Technology has revolutionized orthopedic care with Robotic Knee Replacement Surgery.
In this method, the surgeon uses a robotic-assisted system to plan and execute the procedure with millimeter accuracy. Pre-operative scans create a 3D model of the patient’s knee, helping surgeons determine the perfect implant size, alignment, and positioning before making any incision.
The robot doesn’t replace the surgeon—it enhances precision by guiding every movement, ensuring optimal balance and symmetry for each individual’s anatomy.
Key benefits:
- Greater accuracy and customization
- Less bone loss and tissue damage
- Reduced pain and faster rehabilitation
- Longer implant lifespan
Best for: Patients looking for cutting-edge, personalized joint replacement solutions that minimize risks and improve outcomes.
4. Titanium Knee Replacement – Strength and Longevity Combined
Titanium Knee Replacement uses implants made from high-quality titanium alloys, known for their strength, corrosion resistance, and biocompatibility. Titanium is lighter than other metals and integrates well with human bone, reducing allergic reactions and inflammation risks.
This material is ideal for patients seeking long-term durability with the most natural feel possible. Many titanium implants last over 20 years, even in active individuals.
Key benefits:
- Long-lasting durability and wear resistance
- Suitable for metal-sensitive patients
- Lightweight and comfortable for movement
- Excellent biocompatibility
Best for: Younger or highly active individuals who need a robust, allergy-friendly implant.
5. Minimally Invasive Knee Replacement – Faster Healing, Smaller Scars
In a Minimally Invasive Knee Replacement, the same replacement is performed through smaller incisions than traditional methods. Special instruments allow the surgeon to operate without cutting through large muscles, which significantly shortens recovery time.
This approach can be used in both total and partial replacements, making it a popular choice among patients who want a quicker return to daily activities.
Key benefits:
- Reduced post-operative pain and scarring
- Quicker discharge and rehabilitation
- Lower blood loss and infection risk
- Early return to normal activities
Best for: Patients with moderate arthritis who want a shorter hospital stay and faster recovery period.
How to Know Which Type of Surgery Is Right for You
The right type of knee replacement depends on several factors:
- Extent of damage: Whether one or multiple compartments of the knee are affected.
- Age and activity level: Younger, more active patients may benefit from partial or minimally invasive options.
- Bone quality and alignment: Determines the type of implant and approach required.
- Previous surgeries or injuries: May influence whether robotic assistance or titanium implants are used.
Your orthopedic evaluation will typically include physical examination, X-rays, MRI scans, and a review of your medical history. Based on these findings, the surgeon recommends the most suitable approach to restore long-term function and comfort.
What to Expect After Surgery
Regardless of which type of replacement is chosen, post-surgery recovery plays a vital role in long-term success.
Patients are usually encouraged to walk with support within 24 hours. Physiotherapy focuses on regaining range of motion and muscle strength. Most people return to daily activities within 4–6 weeks, while complete healing may take 3–6 months.
Maintaining a healthy weight, following physiotherapy routines, and avoiding high-impact activities help extend the life of the implant and preserve joint mobility.
The Bottom Line
Today’s knee replacement options are more advanced, precise, and customizable than ever. Whether you choose a traditional Total Knee Replacement, a focused Partial Knee Replacement, or a high-tech Robotic Knee Replacement Surgery, the ultimate goal is the same—pain-free movement and better quality of life.
Discussing your needs, goals, and expectations with your orthopedic specialist ensures that the chosen procedure aligns perfectly with your condition, lifestyle, and recovery goals.